What you’ll explore:
In this blog, you will explore the different types of brands, discuss the challenges you will face, learn from brand failures, and tips & tricks for effective branding. Dive into the world of successful brands and discover valuable insights for building your own.
a. Types of brands
Brands can be classified into different types based on various criteria. Here are some of the most common types of brands:
- Product brands: A product brand is a type of brand that represents a specific product, such as Coca-Cola, Nike, or Apple. These brands are often associated with quality, reliability, and innovation.
- Service brands: A service brand is a brand that represents a specific service, such as FedEx, Visa, or Amazon Prime. These brands are often associated with efficiency, speed, and convenience.
- Corporate brands: A corporate brand is a brand that represents a company, such as McDonald’s, GE, or Toyota. These brands are often associated with trust, stability, and reputation.
- Personal brands: A personal brand is a brand that represents an individual, such as Oprah Winfrey, Elon Musk, or Gary Vaynerchuk. These brands are often associated with expertise, charisma, and authenticity.
- Family brands: A family brand is a brand that represents a group of products or services under a common name, such as Procter & Gamble, Nestlé, or General Motors. These brands are often associated with diversity, trust, and value.
- Umbrella brands: An umbrella brand is a brand that represents a variety of products or services that are not necessarily related, such as Virgin, Samsung, or Unilever. These brands are often associated with innovation, creativity, and versatility.
- Co-brands: Co-brands are brands that are created by two or more companies, such as Adidas and Porsche, or Disney and Target. These brands are often associated with complementary strengths, shared values, and increased visibility.
- Luxury brands: Luxury brands are brands that are associated with high-end products or services, such as Chanel, Rolex, or Rolls-Royce. These brands are often associated with exclusivity, prestige, and sophistication.
- Economy brands: Economy brands are brands that are associated with low-cost products or services, such as Walmart, Ryanair, or McDonald’s. These brands are often associated with affordability, accessibility, and simplicity.
- Green brands: Green brands are brands that are associated with sustainable and environmentally friendly products or services, such as Tesla, Patagonia, or The Body Shop. These brands are often associated with responsibility, ethics, and social awareness.
These are some of the most common types of brands, but there are many more that can be classified based on different criteria, such as geographical location, target audience, or marketing strategy.
- Regional brands: Regional brands are brands that are specific to a particular region or area, such as In-N-Out Burger (California), Tim Hortons (Canada), or Vegemite (Australia).
- National brands: National brands are brands that are recognized and sold throughout a country, such as Coca-Cola, Nike, or Toyota.
- Global brands: Global brands are brands that are recognized and sold throughout the world, such as McDonald’s, Apple, or Coca-Cola.
- Brand extensions: Brand extensions are new products or services that are introduced under an existing brand name, such as Nike Golf, Coca-Cola Zero, or Apple Music.
- Private labels: Private labels are brands that are owned and sold by a retailer or distributor, such as Kirkland Signature (Costco), Great Value (Walmart), or 365 Everyday Value (Whole Foods).
- Licensed brands: Licensed brands are brands that are owned by one company but licensed to another company to use, such as Disney characters on children’s clothing, NFL logos on sports apparel, or Hello Kitty on school supplies.
- Ingredient brands: Ingredient brands are brands that are used as a component or ingredient in other products, such as Intel inside computers, Gore-Tex in outdoor apparel, or Dolby in home theater systems.
- Online brands: Online brands are brands that exist only or primarily in the digital space, such as Amazon, Google, or Facebook.
- Start-Up Brands: Start-up brands are brands that are new and emerging, often associated with entrepreneurship, innovation, and disruption, such as Uber, Airbnb, or Casper.
- Legacy brands: Legacy brands are brands that have been around for a long time and have established a reputation and history, such as Ford, Levi’s, or Coca-Cola.
- Celebrity brands: Celebrity brands are brands that are associated with a celebrity, such as Kylie Cosmetics, Gwyneth Paltrow’s Goop, or Jay-Z’s Roc Nation.
- Non-Profit brands: Non-profit brands are brands that represent charitable organizations, such as the American Red Cross, UNICEF, or Oxfam.
- Cause-related brands: Cause-related brands are brands that support a particular cause, such as breast cancer awareness, environmental sustainability, or LGBTQ+ rights.
- Cultural brands: Cultural brands are brands that are associated with a particular culture or lifestyle, such as Patagonia, Harley-Davidson, or Supreme.
- Sports brands: Sports brands are brands that are associated with sports and athletic performance, such as Nike, Adidas, or Under Armour.
- Educational brands: Educational brands are brands that represent educational institutions or programs, such as Harvard University, Coursera, or Rosetta Stone.
- Government brands: Government brands are brands that represent government agencies or programs, such as NASA, the U.S. Postal Service, or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
- Artistic brands: Artistic brands are brands that represent artists or artistic works, such as Yayoi Kusama, Banksy, or the Museum of Modern Art.
- Medical brands: Medical brands are brands that represent medical products or services, such as Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, or Mayo Clinic.
- Retail brands: Retail brands are brands that represent retail stores or chains, such as Walmart, Target, or Best Buy.
- Luxury brands: Luxury brands are brands that are associated with high-end or exclusive products and services, such as Chanel, Rolex, or Louis Vuitton.
- Value brands: Value brands are brands that offer low-priced products or services, often aimed at price-sensitive consumers, such as Dollar General, Walmart’s Great Value, or Costco’s Kirkland Signature.
- Challenger brands: Challenger brands are brands that are relatively new to a market and compete with established brands by offering a unique value proposition or disrupting traditional marketing strategies, such as Tesla, Dollar Shave Club, or Warby Parker.
- Innovation brands: Innovation brands are brands that are known for their innovative products or services, such as Apple, Tesla, or Amazon.
- Iconic brands: Iconic brands are brands that have become symbols of a particular culture or time period, such as Coca-Cola, McDonald’s, or Apple.
- Crowdsourced brands: Crowdsourced brands are brands that involve consumers in the product development process, such as Lego, Threadless, or Starbucks’ My Starbucks Idea platform.
- Green brands: Green brands are brands that promote environmental sustainability and responsibility, such as Patagonia, The Body Shop, or Burt’s Bees.
- Convenience brands: Convenience brands are brands that offer products or services that are easy to access or use, such as 7-Eleven, Uber, or Grubhub.
- Disruptive brands: Disruptive brands are brands that challenge established norms or business models and offer a new approach to a product or service, such as Airbnb, Uber, or Netflix.
- Emotional brands: Emotional brands are brands that appeal to consumers’ emotions and values, such as Dove’s Real Beauty campaign, Always’ Like a Girl campaign, or Coca-Cola’s Share a Coke campaign.
These are some additional types of brands that exist, and each brand type has unique characteristics, challenges, and opportunities.
b. Challenges & the failure you face as a beginner
Branding is the art of creating a unique identity for a business or product. It involves a complex set of skills, ranging from design to marketing, and requires a deep understanding of consumer behaviour and market trends. For beginners, learning about branding can be a daunting task. Here are some of the challenges and failures that beginners may encounter while learning about brand and branding.
- Understanding the concept of branding: One of the biggest challenges beginners face when learning about branding is understanding the concept itself. Branding is not just about creating a logo or a tagline. It’s about creating a unique identity that resonates with consumers and sets a business apart from its competitors. Beginners may struggle to grasp this concept and may find it challenging to create a brand identity that truly reflects the business’s values and mission.
- Creating a brand strategy: Another challenge beginners face is creating a brand strategy that aligns with the business’s goals and objectives. A brand strategy involves defining the target audience, identifying the brand’s unique selling proposition, and developing a messaging framework that communicates the brand’s value proposition to consumers. Beginners may struggle to create a cohesive brand strategy that effectively communicates the brand’s message to the target audience.
- Designing a brand identity: Designing a brand identity is another challenge that beginners may face. Creating a logo, selecting colors, and choosing fonts that represent the brand can be a daunting task. Beginners may struggle to create a visually appealing brand identity that effectively communicates the brand’s values and mission.
- Developing a consistent brand voice: Consistency is key when it comes to branding. A brand voice is the tone and style that a brand uses to communicate with its target audience. Developing a consistent brand voice across all marketing channels is crucial for creating a cohesive brand identity. Beginners may find it challenging to develop a consistent brand voice that effectively communicates the brand’s values and resonates with the target audience.
- Measuring brand success: Measuring the success of a brand is another challenge that beginners may face. Brand success is not just about revenue or profit. It’s about creating a brand that resonates with consumers and builds long-term relationships. Beginners may struggle to identify the right metrics to measure brand success and may find it challenging to track and analyze these metrics over time.
- Fear of failure: Finally, fear of failure is a common challenge that beginners may face when learning about brand and branding. Branding is a complex and challenging field, and it’s natural to make mistakes along the way. Beginners may fear failure and may be hesitant to take risks and try new things. However, failure is an essential part of the learning process, and it’s important to embrace failure as a learning opportunity.
In conclusion, learning about brands and branding can be challenging, but it’s also an incredibly rewarding experience. By understanding the challenges and failures that beginners may face, aspiring brand builders can prepare themselves for success and build brands that resonate with consumers and stand the test of time.
c. How to overcome
Overcoming the challenges of learning about brand and branding requires a combination of persistence, creativity, and a willingness to learn. Here are some tips for overcoming the challenges of learning about branding:
- Understand the basics: Begin by understanding the basics of branding, including what it is, why it’s important, and the different elements that make up a brand. You can find many online resources, courses, and books that can help you gain a solid understanding of the fundamentals of branding.
- Conduct research: Research is crucial in branding. Conduct research to learn about your target audience, competitors, market trends, and consumer behavior. This will help you develop a brand strategy that aligns with the needs and preferences of your target audience.
- Seek inspiration: Seek inspiration from other successful brands in your industry. Analyze their branding strategies, design elements, messaging, and target audience. This can help you better understand how successful brands operate and inspire you to develop your unique brand identity.
- Develop a brand strategy: Develop a brand strategy that aligns with your business’s goals and objectives. Your brand strategy should include a target audience, a unique selling proposition, messaging framework, and visual identity guidelines.
- Consistency is key: Consistency is key when it comes to branding. Make sure your brand messaging and visual identity are consistent across all marketing channels. This helps to create a cohesive brand identity that resonates with your target audience.
- Measure success: Identify the metrics that are most important for measuring the success of your brand. Track these metrics over time and make adjustments to your brand strategy as needed.
- Embrace failure: Embrace failure as a learning opportunity. Be open to trying new things and taking risks. If you make mistakes along the way, use them as an opportunity to learn and improve your branding skills.
In conclusion, learning about brands and branding requires a combination of persistence, creativity, and a willingness to learn. By following the above tips, aspiring brand builders can overcome the challenges of learning about branding and create brands that resonate with consumers and stand the test of time.
d. Tips & Tricks
Building a brand is a complex process that requires a combination of strategy, creativity, and persistence. Here are some tips and tricks to help you build or create a brand that stands out in today’s competitive marketplace:
- Define your brand’s unique value proposition: Your brand’s unique value proposition is what sets it apart from competitors. Identify what makes your brand different and focus on highlighting those unique aspects in your branding strategy.
- Identify your target audience: Understand who your target audience is, their needs, preferences, and pain points. This will help you tailor your branding strategy to resonate with your target audience and build strong relationships with them.
- Develop a brand strategy: Develop a brand strategy that includes a clear mission statement, brand values, messaging, visual identity guidelines, and marketing channels. Your brand strategy should be aligned with your business goals and objectives.
- Create a memorable visual identity: Your brand’s visual identity includes your logo, color scheme, typography, and imagery. These elements should be memorable, unique, and reflective of your brand’s values and mission.
- Consistency is key: Consistency is critical in building a strong brand. Ensure your branding elements, messaging, and tone of voice are consistent across all marketing channels, from social media to print ads.
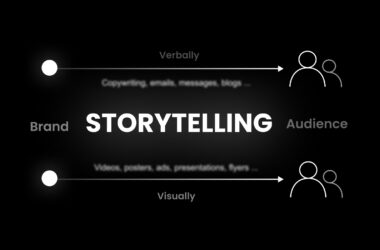
- Use storytelling: Storytelling is a powerful tool in building a brand. Use storytelling to convey your brand’s mission, values, and unique selling proposition in a way that resonates with your target audience.
- Engage with your audience: Engage with your audience through social media, email marketing, and other communication channels. Respond to their questions, comments, and feedback promptly, and build a strong community around your brand.
- Leverage influencers: Leverage influencers to increase brand awareness and reach a broader audience. Identify influencers who align with your brand’s values and mission and build relationships with them.
- Measure success: Measure the success of your branding strategy by tracking metrics such as website traffic, social media engagement, and customer feedback. Use this data to make adjustments to your branding strategy and improve its effectiveness over time.
In conclusion, building any type of brand requires a combination of strategy, creativity, and persistence. By following these tips and tricks, you can build or create a brand that resonates with your target audience and stands out in today’s competitive marketplace.
Did we miss anything, if yes, share your ideas by mentioning us on Threads or on Twitter at @darklionstudio or read the next blog, where you get to what brand design actually is!





synthroid 15 mcg