What you’ll explore:
Welcome to the world of brand design, where strategy, creativity, and marketing converge to shape the success of brands.
Introduction: What is brand design?
In the dynamic and ever-evolving world of business, brand design has evolved into a multifaceted discipline that goes far beyond mere visual aesthetics. It encompasses an array of strategic and creative practices aimed at cultivating a powerful and impactful brand presence. From meticulous research and strategic planning to meticulous design and ongoing management, brand design orchestrates a symphony of elements that shape a brand’s identity and its relationship with its audience.
At its foundation, brand design begins with thorough brand research and strategy. It involves delving deep into the target market, understanding consumer behaviours and preferences, and uncovering the unique value propositions that set a brand apart. This phase lays the groundwork for developing a comprehensive brand strategy that guides all subsequent design and marketing decisions.
Design and development form the artistic core of brand design. This encompasses not only the visual elements but also the overall sensory experience and messaging conveyed by the brand. From crafting captivating logos, selecting harmonious color palettes, and choosing expressive typography, to creating compelling narratives and designing intuitive user interfaces, every detail is carefully curated to create an immersive brand experience.
However, the reach of brand design extends well beyond the realm of aesthetics. Effective marketing and advertising play a pivotal role in elevating a brand’s visibility and establishing a deep connection with the target audience. Brand designers collaborate with marketers to develop innovative campaigns and strategic communication initiatives that amplify the brand’s voice across various channels, from traditional media to digital platforms.
Once a brand’s identity and messaging have been established, brand design shifts gears to encompass the ongoing management and maintenance of the brand. This involves consistently monitoring the brand’s performance, assessing customer feedback, and adapting strategies to stay relevant in a dynamic marketplace. A brand designer’s work is never complete; it is an ongoing process of refining and enhancing the brand’s presence to meet the evolving needs and expectations of its audience.
1. Brand research & strategy: The foundation of effective brand design
At the heart of every successful brand design initiative lies a comprehensive brand research and strategy phase. This critical stage sets the groundwork for all subsequent design decisions and serves as the compass that guides the brand’s journey toward establishing a strong and resonant identity.
Brand research involves delving deep into the intricacies of:
- the target market,
- understanding consumer behaviour, and
- gaining insights into the competitive landscape
- market analysis,
- brand designers identify trends,
- uncover unmet needs, and
- gain a profound understanding of the target audience’s desires and aspirations.
This research serves as the bedrock upon which the brand design strategy is built.
With the insights gained from research, brand designers embark on the strategic planning process. This phase involves defining:
- Purpose,
- Vision
- Mission
- Values
- Brand’s positioning
It clarifies the brand’s unique value proposition and identifies its key differentiators in the marketplace. A well-crafted brand strategy lays the foundation for building a strong and cohesive brand identity that resonates with the target audience.
During the strategic planning process, brand designers also outline the brand’s personality and tone of voice. They determine the emotional attributes that the brand should evoke in its audience and develop a clear messaging framework that aligns with the brand’s positioning and resonates with its target market. This strategic thinking ensures that the brand’s visual and verbal communication is consistent, compelling, and in harmony with its intended perception.
Moreover, brand research and strategy encompass the exploration of various touchpoints and channels through which the brand will interact with its audience. This includes considering both traditional and digital platforms, as well as physical spaces if applicable. Understanding the audience’s preferences and behaviours in these different contexts allows brand designers to tailor the brand experience accordingly, ensuring maximum impact and engagement.
By investing time and effort in brand research and strategy, organizations gain a profound understanding of their target market and are better equipped to design a brand that truly connects with their audience. This research-driven approach minimizes the risk of misalignment and enables brands to differentiate themselves effectively in a crowded marketplace.
In the following sections, we will explore how brand research and strategy inform the design and development stages of brand design, as well as the critical role of marketing and advertisement in amplifying the brand’s message and presence. Together, these elements form a holistic approach to brand design that empowers organizations to forge meaningful connections with their audience and thrive in a competitive business environment.
2. Design & development: Giving life to the brand vision
Once the foundation of brand research and strategy has been laid, the design and development phase takes centre stage, breathing life into the brand’s vision and translating it into tangible visual and experiential elements.
a. Visual identity design:
One of the key aspects of brand design is the creation of a compelling visual identity. This involves designing a logo that embodies the essence of the brand and serves as its visual cornerstone. The logo should encapsulate the brand’s values, personality, and unique positioning, while also being visually appealing and easily recognizable. Alongside the logo, brand designers carefully select color palettes, typography, and graphic elements that align with the brand’s desired image and resonate with the target audience.
Brand designers also extend the visual identity into various brand collateral such as stationery, packaging, website design, and marketing materials. Consistency is crucial in maintaining a cohesive brand presence across different touchpoints, ensuring that the visual elements work harmoniously together to create a distinct and memorable brand experience.
Download the checklist for Visual Identity Design
b. Brand experience design:
Brand design goes beyond visual aesthetics—it encompasses the overall brand experience. Every interaction a customer has with a brand should be purposefully designed to evoke specific emotions, build trust, and leave a lasting impression. Brand designers strategically consider the user journey, ensuring that each touchpoint aligns with the brand’s identity and delivers a consistent experience.
Whether it’s the layout and navigation of a website, the packaging, and unboxing experience, or the interior design of a physical store, brand designers carefully craft the environment in which customers engage with the brand. By paying attention to details, sensory cues, and the overall ambience, they create an immersive brand experience that resonates with the target audience and strengthens the brand-customer relationship.
c. Content creation:
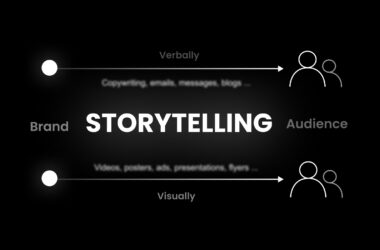
Effective brand design involves developing compelling and relevant content that communicates the brand’s values, story, and offerings. This includes copywriting, photography, videography, and other forms of media. Brand designers work closely with content creators to ensure that the messaging and visuals align with the brand’s voice and resonate with the intended audience. Consistent and authentic storytelling helps to build a strong emotional connection with customers, fostering loyalty and advocacy.
d. Usability and Functionality:
In an increasingly digital world, brand design encompasses the usability and functionality of digital platforms and interfaces. Brand designers collaborate with user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) designers to create intuitive and user-friendly digital experiences that align with the brand’s identity and meet the needs of the target audience. From website navigation to mobile app interfaces, every interaction is meticulously designed to enhance usability and provide a seamless brand experience.
By weaving together these design elements, brand designers give form to the brand’s identity, values, and messaging. They create a visual and experiential language that captivates audiences, strengthens brand recognition, and fosters meaningful connections. In the next section, we will explore how brand design collaborates with marketing and advertising to amplify the brand’s presence and engage the target audience effectively.
3. Marketing & advertising: Amplifying the brand’s message
In the ever-expanding digital landscape and highly competitive marketplaces, effective marketing and advertising are essential components of successful brand design. They play a vital role in amplifying the brand’s message, increasing its visibility, and engaging the target audience on various platforms and channels.
a. Strategic messaging and communication:
Marketing and advertising strategies are built upon the foundation of the brand’s research and strategy. Brand designers work closely with marketing professionals to develop compelling messaging that aligns with the brand’s positioning, values, and target audience. They craft narratives that resonate with customers, communicate the brand’s unique value proposition, and elicit desired emotional responses.
Through consistent and strategic messaging, brand designers ensure that the brand’s voice remains cohesive across different marketing channels. From social media posts and blog content to advertising campaigns and public relations efforts, every communication piece is an opportunity to reinforce the brand’s identity and build brand awareness.
b. Digital marketing:
In today’s digital age, brand design integrates seamlessly with digital marketing strategies. Brand designers collaborate with digital marketers to leverage online platforms, such as social media, search engine optimization (SEO), and content marketing, to reach and engage a broader audience.
Social media platforms offer an avenue for brand designers to visually express the brand’s personality, share valuable content, and interact directly with customers. By crafting visually appealing and consistent posts, infographics, and videos, brand designers create an immersive brand experience that captures attention and encourages audience participation.
Search engine optimization ensures that the brand’s website and content rank well in search engine results, increasing visibility and driving organic traffic. Brand designers collaborate with SEO experts to optimize the website’s design, structure, and content, ensuring a seamless user experience and effective conversion.
Content marketing, including blogs, articles, and videos, allows brand designers to share valuable and engaging content that educates, entertains, or inspires the target audience. By providing relevant and high-quality content, brands can position themselves as industry leaders and build trust and credibility among their audience.
c. Traditional marketing:
While digital marketing has become increasingly prominent, traditional marketing channels still play a significant role in brand design. Print advertisements, billboards, television commercials, and radio spots provide opportunities for brand designers to create impactful visuals and memorable messages that capture attention and leave a lasting impression.
Brand designers understand the nuances of different traditional marketing channels and work closely with advertising agencies to develop captivating visuals and persuasive copy that align with the brand’s identity and objectives. By carefully selecting the right traditional marketing channels and tailoring the creative assets to each medium, brand designers maximize the brand’s reach and impact.
d. Integrated campaigns:
Brand designers collaborate with marketing teams to develop integrated marketing campaigns that align with the brand’s strategy and deliver a unified message across multiple channels. By combining digital and traditional marketing tactics, these campaigns create a cohesive and immersive brand experience that resonates with the target audience at various touchpoints.
Through integrated campaigns, brand designers strive to create a seamless transition between online and offline experiences, fostering brand consistency and reinforcing the brand’s identity in the minds of consumers.
In conclusion, marketing and advertising are integral components of brand design, working in tandem to amplify the brand’s message and engage the target audience. By crafting strategic messaging, leveraging digital marketing channels, utilizing traditional marketing platforms, and developing integrated campaigns, brand designers ensure that the brand’s voice is heard, its presence is felt, and its story resonates with the hearts and minds of customers.
4. Manage & maintenance: Sustaining brand excellence
Brand design is not a one-time endeavour but an ongoing process that requires careful management and maintenance to ensure the brand remains relevant, consistent, and aligned with its objectives. This section explores the crucial role of brand management in sustaining brand excellence over time.
a. Consistent brand guidelines:
Brand designers establish comprehensive brand guidelines that serve as a reference for all brand-related activities. These guidelines outline the proper usage of the brand’s visual elements, including the logo, colors, typography, and imagery. By providing clear instructions and specifications, brand designers ensure consistency in the brand’s visual identity across different platforms and communication materials.
Brand guidelines also encompass messaging guidelines, including tone of voice, key messaging points, and brand storytelling principles. These guidelines help maintain a consistent brand voice and ensure that all brand communications align with the brand’s positioning and values.
b. Monitoring brand performance:
Brand designers closely monitor the performance and perception of the brand in the market. This involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), conducting market research, and gathering customer feedback. By analyzing data and insights, brand designers gain valuable information about the brand’s strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement.
Through continuous monitoring, brand designers can identify emerging trends, shifts in customer preferences, and changes in the competitive landscape. This information informs strategic decisions and enables brands to adapt their design, messaging, and marketing efforts to remain relevant and competitive.
c. Evolution and adaptation:
As markets and customer expectations evolve, brands must adapt to stay ahead. Brand designers play a pivotal role in assessing the need for brand evolution or refinement. They analyze market trends, consumer insights, and competitive benchmarks to identify opportunities for brand enhancement or adaptation.
Brand designers collaborate with stakeholders to strategically evolve the brand’s visual identity, messaging, or brand experience while staying true to its core essence. This may involve refreshing the visual elements, updating brand messaging to align with shifting market dynamics, or even repositioning the brand to better connect with the target audience.
d. Brand communication and internal alignment:
Effective brand design relies on strong internal alignment and consistent brand communication across all levels of an organization. Brand designers work with internal teams to ensure that everyone understands and embodies the brand’s values, positioning, and messaging.
They develop internal brand communication strategies and materials to educate employees about the brand’s identity and provide guidance on brand representation. By fostering a shared understanding and a sense of ownership, brand designers empower employees to become brand ambassadors who consistently deliver a unified brand experience.
e. Brand crisis management:
Brand designers are instrumental in managing and mitigating brand crises. In times of crisis or negative publicity, they collaborate with communication and PR teams to develop strategies that protect the brand’s reputation and minimize potential damage. They create crisis communication materials, manage brand messaging, and guide the organization on navigating challenging situations while staying true to the brand’s values and objectives.
Brand designers also play a crucial role in ensuring that brand management extends to external partnerships and collaborations. They provide guidance and oversight to third-party vendors or partners to maintain consistency and protect the brand’s integrity when working on joint initiatives.
In conclusion, brand management is an ongoing responsibility that ensures the brand’s consistency, relevance, and adaptability over time. By adhering to brand guidelines, monitoring brand performance, evolving and adapting as needed, fostering internal alignment, and effectively managing crises, brand designers safeguard the brand’s integrity and contribute to its long-term success.
Conclusion:
In summary, brand design encompasses the strategic development, creative design, and ongoing management of a brand’s identity. It goes beyond visual aesthetics to create a cohesive and impactful brand experience. Brand designers play a crucial role in crafting compelling visuals, strategic messaging, and engaging marketing campaigns that resonate with the target audience. By continuously monitoring and adapting the brand, they ensure its consistency, relevance, and long-term success in the competitive market.





RtQPsIkrMTB